CP-Symbols Electrical
 CP-Symbols
CP-Symbols
Electrical
Electrics – IEC, NFPA includes symbols in accordance with en 60617 and NFPA 79 standards.
 |
Electrics – IEC, NFPA contains the following categories of symbols:
|
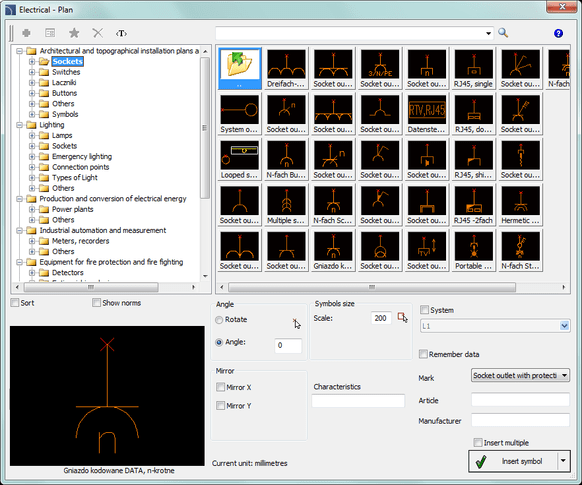
Electrical – The plan includes symbols for the design of electrical circuits on architectural plans.
|
Electrics – The plan contains the following categories of symbols:
|
 |
Electrics – The diagram includes symbols for the construction of electrical circuit diagrams.
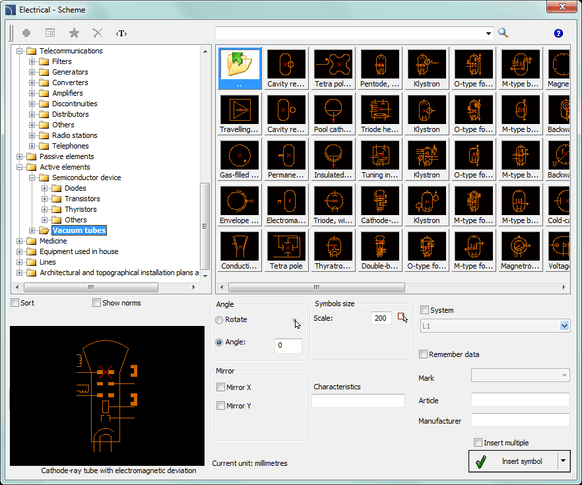 |
Electrics – The scheme contains the following categories of symbols:
|
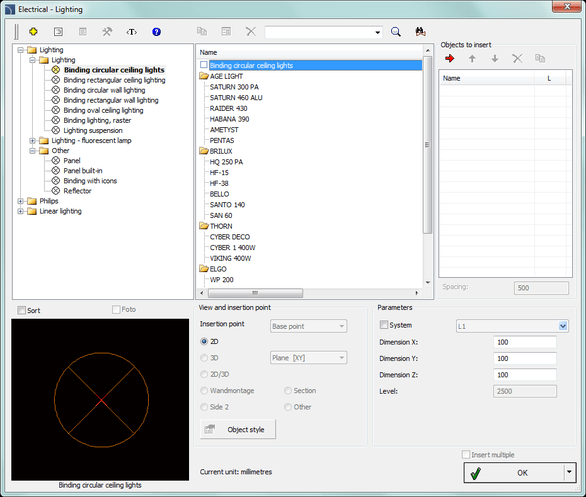
Electrics – Lighting is a database of fixtures.
|
Electrics – Lighting contains the following categories of conventional designations:
|
 |
Flowcharts and diagrams include basic notations used in flowcharts in many industries.
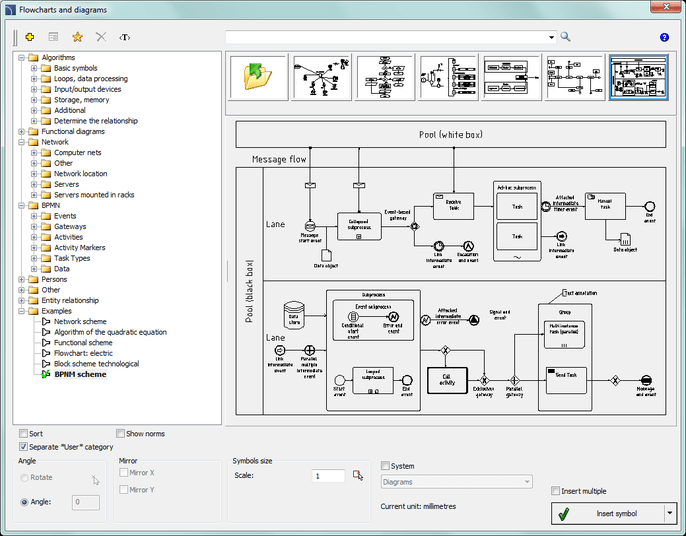 |
Flowcharts and diagrams contain the following categories of legends:
|
|
The CP-Symbols module also contains the following general-purpose commands:
|
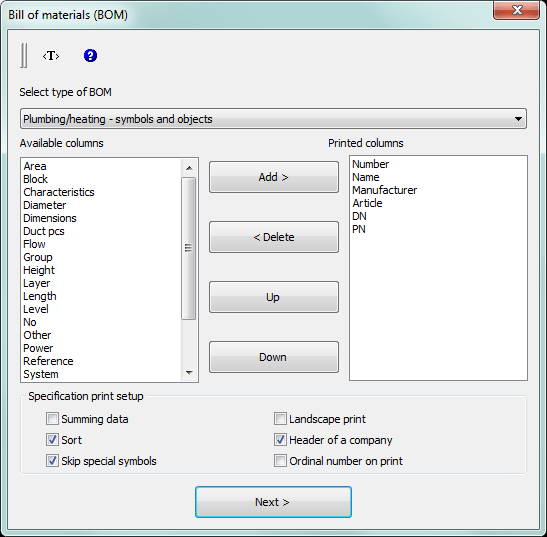 |
CP-Manufacturers |
CP-Symbols |
CADprofi |
|
|
|
Free |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Order now |
|
|
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
Order now |
Where to buy? For purchase inquiries ask us